Picture credit: http://images.ddccdn.com
New research in The FASEB Journal suggests that cigarette smoke interferes with the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator protein, leading to dry, sticky mucus and increased infections
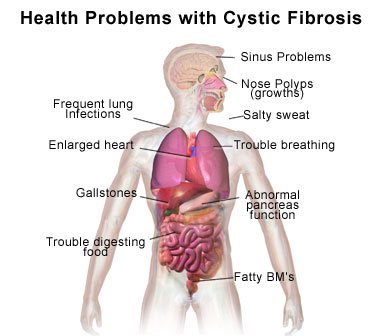
If you smoke cigarettes, you have more in common with someone who has cystic fibrosis than you think. A new research report appearing online in the FASEB Journal shows that smoking cigarettes affects the lungs in a way that is very similar to cystic fibrosis, a life threatening disease affecting the lungs and other organs.
In cystic fibrosis, improper movement of salt and water in the cells lining the lungs causes a thick and sticky mucus to form. Bacteria become trapped in this mucus and thrive, leading to life-threatening lung infections. The FASEB Journal study shows that smoking negatively affects the lungs in a similar way, leading to mucus that causes dry cough, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, among other problems.
"We hope this study will highlight the importance of airway hydration in terms of lung health and that it will help provide a road map for the development of novel therapies for the treatment of smoking-related lung disease," said Robert Tarran, Ph.D., a researcher involved in the work from the Cystic Fibrosis/Pulmonary Research and Treatment Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
To make this discovery, Tarran and colleagues conducted multiple experiments both in humans and in laboratory-grown cells testing the effects of cigarette smoke on the function of a protein that helps the lungs stay hydrated, called "CFTR." They found that people exposed to cigarette smoke had a 60 percent decrease in CFTR activity, compared to those exposed only to clean air. They also exposed human lung cells to either air or cigarette smoke and the measured the level of liquid covering the lung cells. The cells exposed to cigarette smoke had much lower liquid levels, which remained low for at least two and a half hours. Additional studies showed that this was caused by cigarette smoke interfering with CFTR's function. Finally, the researchers found that the addition of hypertonic saline -- a treatment for cystic fibrosis -- to cells exposed to cigarette smoke caused the level of liquid above the cells to increase toward normal levels. The hypertonic saline treatment also increased mucus clearance.
This novel finding suggests that treatments aimed at cystic fibrosis might also help people with smoking-related diseases - and vice versa," said Gerald Weissmann, M.D., Editor-in-Chief of The FASEB Journal.
"But the bottom line remains: the most effective treatment for smoker's cough, or worse, is to quit smoking, now!” adds Weissmann.
<<< * >>>
The above story is reprinted with editorial adaptation by the Zestzfulness Team from materilas provided by Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, via EurekAlert!, a service of AAAS.
The article has been published in the October 11, 2011 online issue of the Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology: Lucy A. Clunes, Catrin M. Davies, Raymond D. Coakley, Andrei A. Aleksandrov, Ashley G. Henderson, Kirby L. Zeman, Erin N. Worthington, Martina Gentzsch, Silvia M. Kreda, Deborah Cholon, William D. Bennett, John R. Riordan, Richard C. Boucher, and Robert Tarran. Cigarette smoke exposure induces CFTR internalization and insolubility, leading to airway surface liquid dehydration. FASEB J fj.11-192377; doi:10.1096/fj.11-192377


No comments:
Post a Comment